Organ System of the Body Defends Again Microbial Pathogens
The Immune Organization
What is the immune system?
The immune system protects your child's body from exterior invaders. These include germs such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, and toxins (chemicals made past microbes). The immune system is made up of different organs, cells, and proteins that piece of work together.
In that location are 2 primary parts of the immune organization:
- The innate immune system. Y'all are born with this.
- The adaptive immune system. Yous develop this when your trunk is exposed to microbes or chemicals released by microbes.
These 2 immune systems work together.
The innate immune system
This is your kid's rapid response arrangement. It is the first to answer when it finds an invader. It is made up of the peel, the centre's cornea, and the mucous membrane that lines the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary tracts. These all create concrete barriers to help protect your kid's body. They protect against harmful germs, parasites (such as worms), or cells (such as cancer). The innate immune organization is inherited. It is active from the moment your child is built-in. When this system recognizes an invader, it goes into action right away. The cells of this immune system surround and cover the invader. The invader is killed inside the immune system cells (called phagocytes).
The caused immune system
The acquired immune system, with assist from the innate organisation, makes special proteins (chosen antibodies) to protect your torso from a specific invader. These antibodies are developed by cells called B lymphocytes after the body has been exposed to the invader. The antibodies stay in your child'southward body. It tin take several days for antibodies to form. But later on the first exposure, the immune system volition recognize the invader and defend against it. The caused immune system changes during your kid'due south life. Immunizations train your child's immune organization to brand antibodies to protect them from harmful diseases.
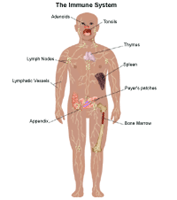
The cells of both parts of the immune system are made in different organs of the trunk, including:
- Adenoids. Two glands located at the back of the nasal passage.
- Bone marrow. The soft, spongy tissue found in bone cavities.
- Lymph nodes. Small organs shaped like beans, which are located all over the torso and connect via the lymphatic vessels.
- Lymphatic vessels. A network of channels all over the torso that carries lymphocytes to the lymphoid organs and bloodstream.
- Peyer patches. Lymphoid tissue in the small-scale intestine.
- Spleen. A fist-sized organ located in the abdomen (intestinal) cavity.
- Thymus. 2 lobes that join in front end of the windpipe (trachea) behind the breastbone.
- Tonsils. Ii oval masses in the back of the throat.
How do antibiotics help fight infections?
Antibiotics can be used to assist your child'southward immune organization fight infections past bacteria. But antibiotics don't work for infections caused past viruses. Antibiotics were developed to impale or disable sure leaner. That ways that an antibiotic that works for a skin infection caused past a certain bacteria may not piece of work to cure diarrhea caused by a different bacteria. Using antibiotics for viral infections or using the wrong antibody to treat a bacterial infection can help bacteria become resistant to the antibiotic so it won't work too in the hereafter. Information technology's important to take antibiotics as prescribed and for the right amount of time. If antibiotics are stopped early on, the bacteria may develop a resistance to the antibiotics. Then the infection may come back once more and be harder to treat.
Most colds and acute bronchitis infections won't respond to antibiotics. You can help subtract the spread of more aggressive leaner past not asking your child's healthcare provider for antibiotics in these cases.
Source: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/the-immune-system#:~:text=What%20is%20the%20immune%20system,and%20proteins%20that%20work%20together.
0 Response to "Organ System of the Body Defends Again Microbial Pathogens"
Post a Comment